Definition For Instantaneous Power

Si unit of power.
Definition for instantaneous power. We often encounter terms like instantaneous average total real reactive apparent and complex power or simply power. Power is defined as rate of doing the work. Such a waveform is described as the parameter as a function of time. The instantaneous power p delivered to the load can be calculated as the sum of the products of the elements or using the euclidean dot product of two vectors as.
Since instantaneous power changes with time it is difficult to measure. The limiting value of average power such that δt approaches to zero is known as instantaneous power. In alternating current circuits energy storage elements such as inductors and capacitors may result in periodic reversals of the direction of energy flow. Instantaneous power in an electric circuit is the rate of flow of energy past a given point of the circuit.
The portion of power that averaged over a complete cycle of the ac waveform results in net transfer of energy in one direction is. If δt approaches to zero then power will be instantaneous and given by. If δw amount of work is done in time interval δt the instantaneous power delivered will be. δw is the work done in short interval of time δt is following the instant t.
This is where average power comes in. The objective of the following analyses is to find a set of optimum minimal total instantaneous transmission losses wire currents that delivers the same instantaneous power p as. The properties and physical meanings of the newly defined instantaneous reactive power are discussed in detail. The instantaneous voltage v current i and power p has a value that corresponds to a specific time t every waveform has an infinity number of instantaneous values.
Instantaneous power delivered to a certain resistance r l or to some resistive medium having equivalent resistance r l by a transient current is defined by relation 4 111 on the other hand the absorbed power in the human body expressed by the field quantities is equivalent to the concept of instantaneous power arising from the circuit theory and it is usually defined as a volume integral. Gives a generalized definition of instantaneous reactive power which is valid for sinusoidal or nonsinusoidal balanced or unbal anced three phase power systems with or without zero sequence currents and or voltages. 4 p n 1 m e n i n e i.

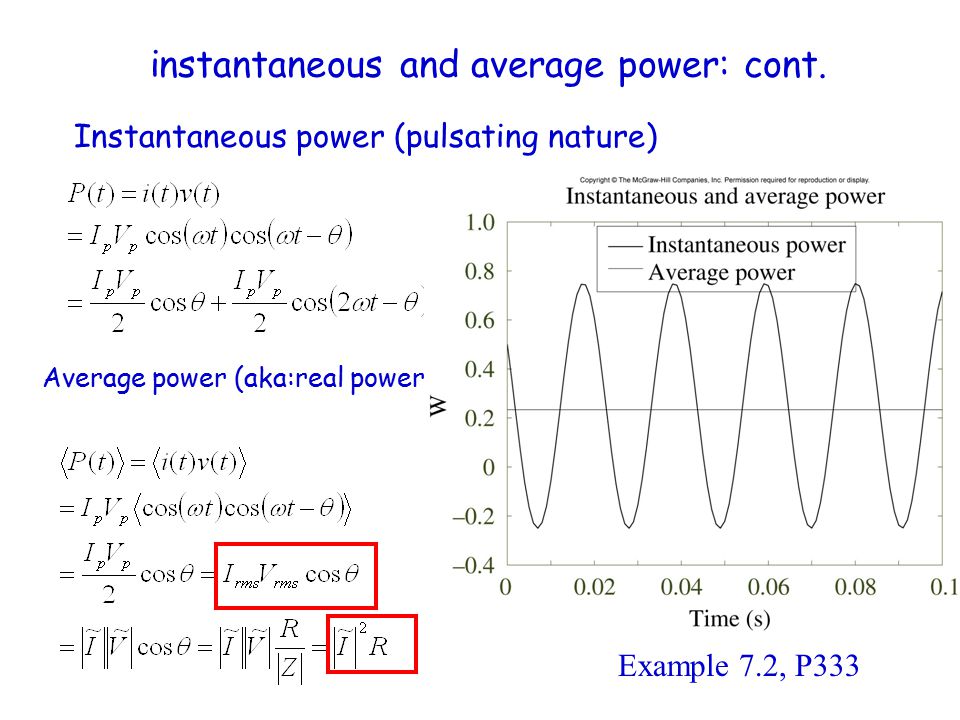
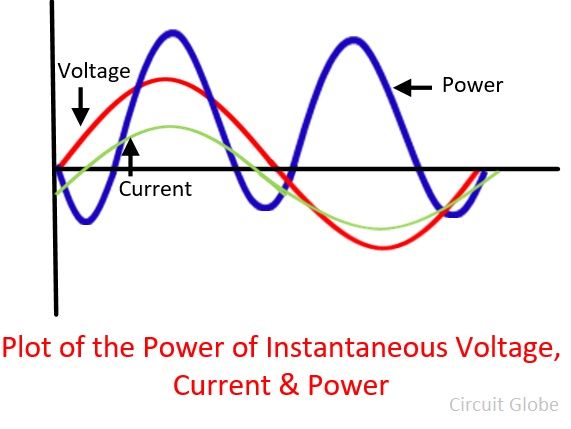




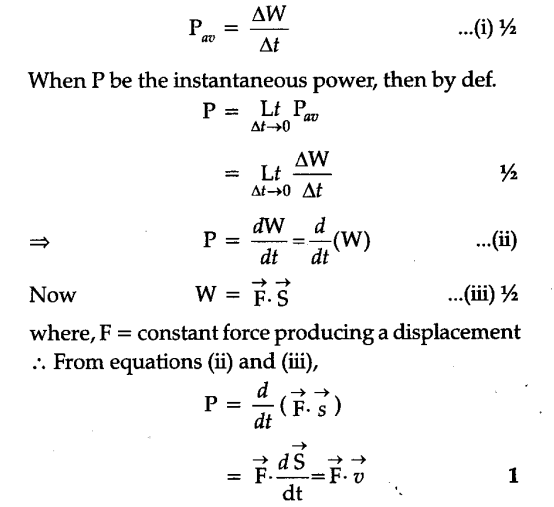
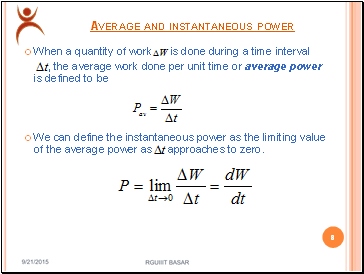






.PNG)


