Endemic Definition In Epidemiology

2002 by the mcgraw hill companies inc.
Endemic definition in epidemiology. 2 for microparasites such as measles endemic refers to an infection that can persist in a population in the long term without reintroduction from outside. Endemic is perhaps most commonly used to describe a disease that is prevalent in or restricted to a particular location region or population. For example malaria is said to be endemic to tropical regions. For example chickenpox is endemic steady state in the united kingdom but malaria is not.
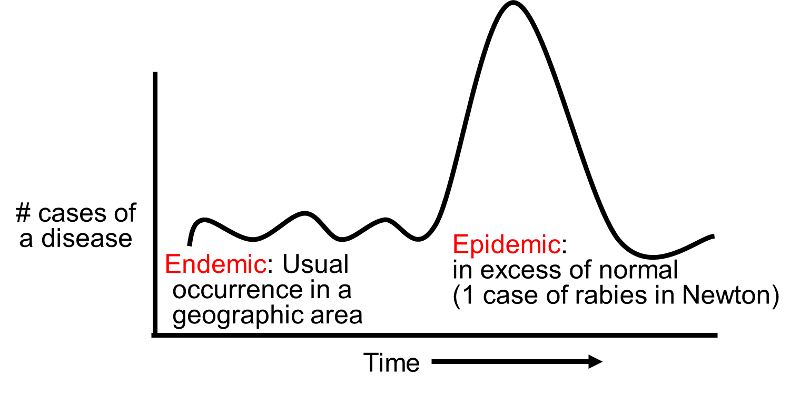
Endemic is the persistence of a particular disease within a geographical region. Endemic diseases are relatively rare and not as widespread as an epidemic. The disease is endemic among british sheep to many british flocks. A characteristic of a particular population environment or region.
Endemic conditions do not exhibit wide fluctuations over time in a defined place. Endemic is an adjective that means natural to native to confined to or widespread within a place or population of people. Enˈdem ɪk especially of a disease or a condition regularly found and very common among a particular group or in a particular area. In epidemiology an infection is said to be endemic from greek ἐν en in within and δῆμος demos people in a population when that infection is constantly maintained at a baseline level in a geographic area without external inputs.
Epidemic disease is the sudden outbreak of the disease in a particular area. Endemic is perhaps most commonly used to describe a disease that is prevalent in or restricted to a particular location region or population. According to the centers for disease control and prevention cdc an endemic refers to the constant presence and or usual prevalence of a disease or infectious agent in a population within a given geographic area. The disease is present in a community at all times but in relatively low frequency.
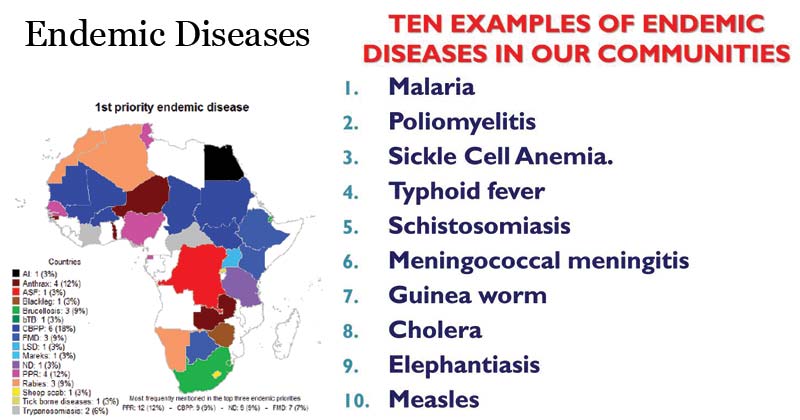
A good example of an endemic in south america and large parts of africa is malaria. Examples of endemic diseases include chicken pox that occurs at a predictable rate among young school children in the united states and malaria in some areas of africa. For example malaria is said to be endemic to tropical regions. Ed also refers to the usual prevalence of a given disease in an area or group mcgraw hill concise dictionary of modern medicine.
Malaria is endemic in many of the hotter regions of the world. Endemic is an adjective that means natural to native to confined to or widespread within a place or population of people.