Definition Of Diffusion Pressure Deficit

Meyer in the year 1938.
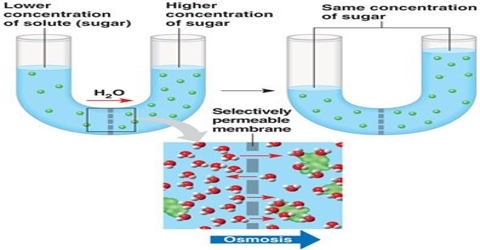
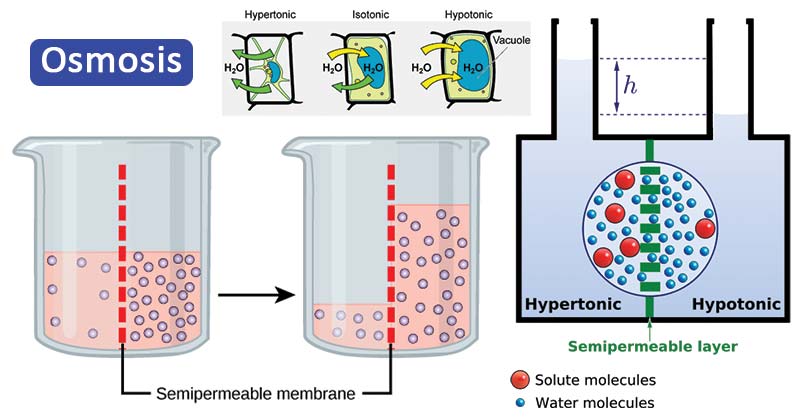
Definition of diffusion pressure deficit. Dpd of pure water is the lowest dilute solution is high concentrated solution is highest. When a plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution water enters into a cell by osmosis and as a result turgor pressure develops in the cell which is in solution. In a plant cell the pressure s equal to the difference between the osmotic pressure p and the turgor pressure t. Dpd was originally called suction pressure.
Diffusion defects refer to deficiencies in oxygen pulmonary gas exchange that yield abnormally low partial pressures of arterial oxygen. If some solute is dissolved in water its diffusion pressure decreases. Diffusion pressure deficit is the reduction in diffusion pressure of the solvent in a system over its pure state. Diffusion pressure deficit is the pressure which opposes the diffusion of water from the region of higher chemical potential to lower chemical potential.
Diffusion pressure deficit d p d. Important points of diffusion pressure deficit. The amount by which diffusion pressure of a solution is lower than its pure solvent is known as diffusion pressure deficit or dpd. The two factors which determine the dpd are osmotic pressure and the turgor pressure.
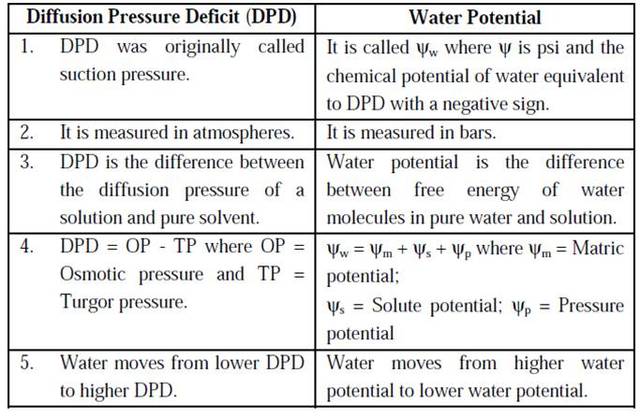
Water potential suction pressure or formerly diffusion pressure deficit dpd the tendency of a cell to draw in water from outside by osmosis the water moving from a higher to a lower water potential. It can be represented by a relation dpd op wall pressure turgor pressure. Answered by lifeeasy authors. As described in oxygen pulmonary gas exchange diffusion of oxygen from the alveolar space to the pulmonary capillaries in a healthy lung is normally perfusion limited this means that the partial pressure of alveolar oxygen largely equilibrates with the blood.
It is measured in atmospheres. The difference between diffusion pressure of pure water and solution is called diffusion pressure deficit dpd. This term was first coined by b s. Diffusion pressure deficit in a plant cell the pressure s equal to the difference between the osmotic pressure p and the turgor pressure t.
Diffusion pressure deficit definition is the algebraic sum of all the forces tending to cause water to move into a plant cell. When the osmotic and turgor pressures are equal the plant does not absorb water.